MapLight Therapeutics investment analysis
October 31, 2023
This is not investment advice. We used AI and automated software tools for most of this research. A human formatted the charts based on data / analysis from the software, prompted the AI to do some editing, and did some light manual editing. We did some fact checking but cannot guarantee the accuracy of everything in the article. We do not have a position in or a relationship with the company.
Overview
San Francisco-based MapLight Therapeutics is a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company developing treatments for central nervous system disorders.
Lead program ML-007C-MA, set for Phase 2 trials in 2024, aims at treating schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease psychosis. This drug combines an M1/M4 muscarinic agonist with an antagonist to reduce peripheral side effects. The substantial prevalence of schizophrenia—impacting approximately 3 million U.S. adults—highlights a significant market opportunity. The company has other programs including ML-007 targeting dyskinesia and ML-004, a 5HT-1b agonist in Phase 2 for social communication deficits in autism spectrum disorder.
The ML-007C-MA program in schizophrenia is compelling based on data from several pivotal trials of competitor Karuna Therapeutics' M1/M4 muscarinic receptor antagonist in schizophrenia. Karuna has a $6B market cap as of October 2023, based largely on the potential of its schizophrenia program. While it is unclear exactly what might differentiate MapLight's approach from Karuna's, the size of the market suggests that a second entrant could still generate significant revenue.
In October 2023, MapLight raised a $225M Series C financing round, led by Novo Holdings with participation from new investors 5AM Ventures and Cowen.
MapLight Therapeutics Pipeline Overview
| Product name | Modality | Target | Indication | Discovery | Preclinical | Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | FDA submission | Commercial | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML-004 | Small molecule | 5HT-1b agonist | Autism Spectrum Disorder sociability / irritability | ||||||||
| ML-007C-MA | Small molecule | M1/M4 muscarinic agonist | Schizophrenia | M1/M4 muscarinic agonist co-formulated with a peripherally selective muscarinic antagonist | |||||||
| ML-007C-MA | Small molecule | M1/M4 muscarinic agonist | Alzheimer's disease psychosis | M1/M4 muscarinic agonist co-formulated with a peripherally selective muscarinic antagonist | |||||||
| ML-007C-MA | Small molecule | M1/M4 muscarinic agonist | Tardive dyskinesia or Levodopa induced dyskinesia | M1/M4 muscarinic agonist co-formulated with a peripherally selective muscarinic antagonist | |||||||
| ML-007 | Small molecule | M1/M4 muscarinic agonist | Tardive dyskinesia or Levodopa induced dyskinesia | ||||||||
| ML-016 | Small molecule | GPR6 antagonist | Parkinson's Disease / Depression | ||||||||
| ML-009 | Small molecule | Undisclosed | Hyperactivity / impulsivity |
Highlights and risks
Clinically validated mechanism of action based on KarXT's, an M1/M4 muscarinic receptor agonist paired with a peripheral antagonist, Phase 2 and 3 clinical data.
Lead asset in Phase 2 with positive Phase 1 and preclinical data
Targeting large markets: prior schizophrenia drugs have generated several billion in peak sales
Significant unmet need for better antipsychotic drugs
Robust pipeline including additional clinical-stage assets
Second-entrant to more advanced competitor KarXT
Targeting high risk indications with historically low probability of success
Schizophrenia has many approved generic medications, and premium pricing requires meaningful differentiation
Valuation
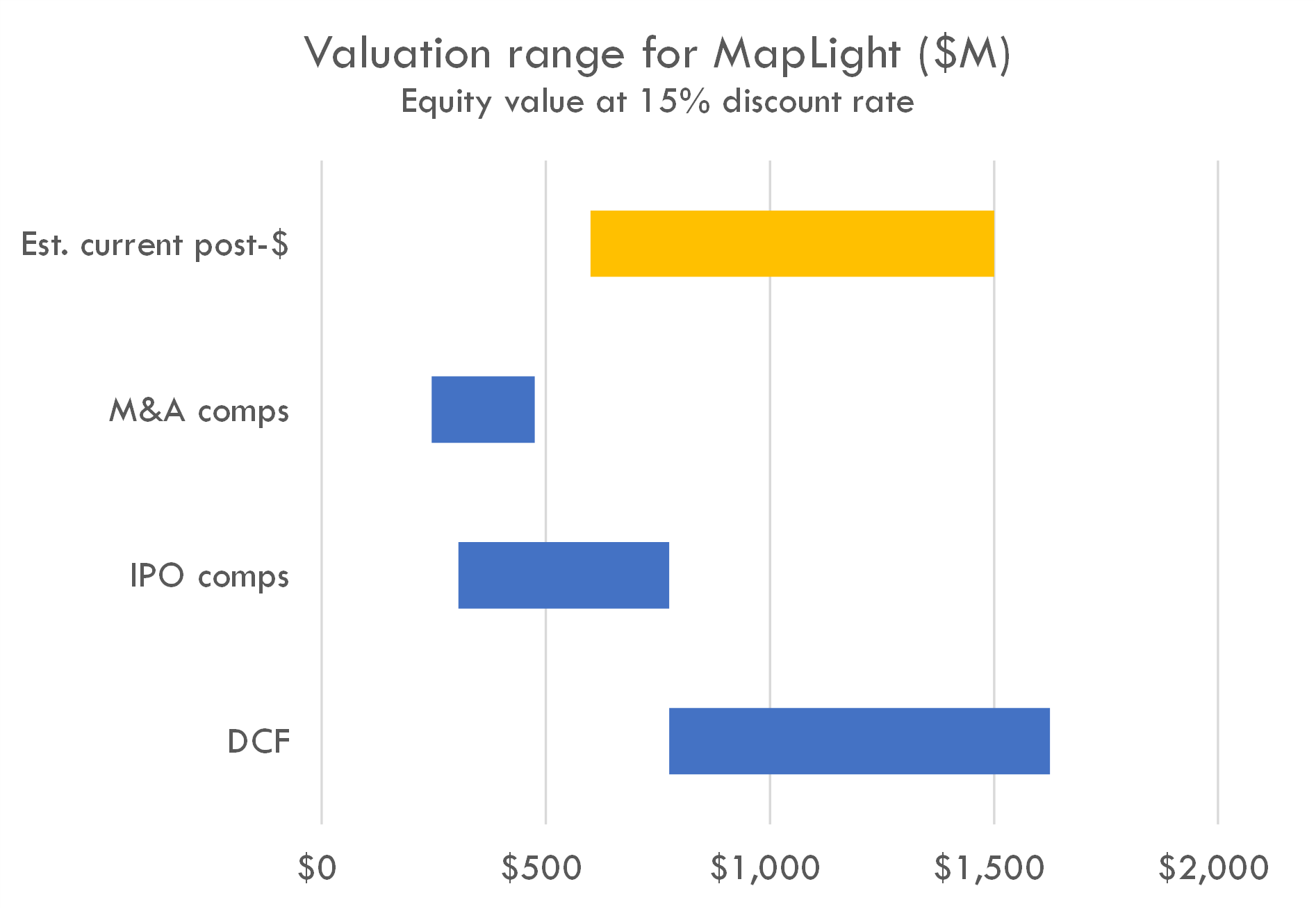
For reference, Karuna Therapeutics (KRTX) is in FDA registration with its M1/M4 muscarinic agonist for schizophrenia and has a market cap of $6B as of October 2023.
Our DCF is based on the revenue assumptions below, with industry benchmarks used for other assumptions, and a 15% discount rate. We used industry standard assumptions for probability of success, but based on KarXT's Phase 3 data (KarXT is a drug with the same mechanism of action as ML-007C-MA in schizophrenia), we assumed a 40% (up from 27%) Phase 2 probability of success and a 70% (up from 56%) probability of success.
The company's estimated post-money valuation is slightly higher than the range suggested by IPO and M&A comps, and in the range suggested by the DCF. Editor's note: This may be a function of the tight IPO market, as one of the inputs to the valuation model is probability of IPO. The DCF yields a high valuation due to the size of the market in schizophrenia and higher than typical probability of success, given KarXT's Phase 3 data. Given how close of a comp KRTX is, and KRTX's $6B market cap, investors likely priced MapLight as a discount to KRTX given MapLight's earlier stage and later entry to market. Pricing at a discount to KRTX could support a valuation near or north of $1B, although a valuation closer to $600-700M is also plausible based on precedent transactions.
Pipeline analysis
ML-007C-MA in schizophrenia
Scientific thesis
Muscarinic receptors, which are a subtype of acetylcholine receptors, have been of interest in treating schizophrenia due to their role in modulating neurotransmission. The M1 and M4 receptors, in particular, are believed to be of significance in treating both the positive (e.g., hallucinations, delusions) and negative (e.g., withdrawal from others, difficulty enjoying life) symptoms of schizophrenia.
The M1 and M4 muscarinic receptors are predominantly found in the brain and have been linked to cognitive functioning and psychosis. Therefore, a compound that can selectively stimulate these receptors might improve symptoms of schizophrenia without causing widespread activation of other muscarinic receptors, which can lead to side effects.
One challenge with developing muscarinic agonists for CNS indications is that stimulating muscarinic receptors outside of the brain can lead to a wide range of side effects. These can include dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, urinary retention, and more. These side effects are often dose-limiting, meaning that it's challenging to achieve a therapeutic effect in the brain without causing intolerable side effects in the rest of the body.
By pairing the M1/M4-preferring muscarinic agonist (ML-007) with a precision-matched muscarinic antagonist, ML-007C-MA seeks to harness the therapeutic benefits of activating these receptors in the brain while blocking the potential side effects outside the brain. This approach allows for a potentially effective CNS therapy without the dose-limiting peripheral side effects.
KarXT validates mechanism of action
KarXT, by Karuna Therapeutics, employs a similar strategy. It combines xanomeline, a muscarinic agonist, with trospium, a muscarinic antagonist that does not easily cross the blood-brain barrier. Thus, KarXT is also designed to stimulate muscarinic receptors in the brain while minimizing side effects outside of it. The Phase 3 results of KarXT validate this strategy, and by extension, provide hope for the success of ML-007C-MA's similar approach.
KarXT has been studied in several Phase 3 studies. Here are some of the highlights:
- Phase 3 EMERGENT-2 Trial
- Primary Endpoint: KarXT showed a statistically significant 9.6-point reduction in the PANSS (Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale) Total Score compared to placebo at Week 5.
- Key Secondary Endpoints: Statistically significant reductions in both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia, as measured by the PANSS subscales:
- 2.9-point reduction in PANSS positive subscale.
- 1.8-point reduction in PANSS negative subscale.
- 2.2-point reduction in PANSS negative Marder factor subscale.
- KarXT was generally well-tolerated with a side effect profile consistent with prior trials. Common side effects included constipation, dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, headache, increased blood pressure, dizziness, gastroesophageal reflux disease, abdominal discomfort, and diarrhea.
- Other Highlights: Early and sustained significant reduction of symptoms from Week 2 through the entire duration of the trial.
- Phase 3 EMERGENT-3 Trial
- Primary Endpoint: KarXT showed a statistically significant 8.4-point reduction in the PANSS Total Score compared to placebo at Week 5.
- Secondary Endpoints: KarXT demonstrated a 3.5-point reduction in PANSS positive subscale at Week 5. Additionally, there were significant reductions in PANSS negative subscale and PANSS negative Marder factor subscale at Week 4.
- Side Effects: KarXT's side effect profile was consistent with previous trials, with common side effects being nausea, dyspepsia, vomiting, constipation, headache, hypertension, diarrhea, and insomnia.
- Other Highlights: Demonstrated an early and sustained significant reduction of symptoms from Week 2 through the end of the trial.
Clinical implications of KarXT data
Across the EMERGENT-2 and EMERGENT-3 trials, KarXT consistently demonstrated statistically and clinically significant reductions in both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
The PANSS (Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale) is a widely used scale for assessing the severity of schizophrenia symptoms. The total score can range from 30 (asymptomatic) to 210 (extremely symptomatic), with subscores for positive, negative, and general psychopathology symptoms. The reductions observied in the trials (EMERGENT-2: 9.6-point reduction and EMERGENT-3: 8.4-point reduction) are clinically significant. In schizophrenia trials, a change of 5-7 points in the PANSS total score is usually considered clinically meaningful. Both trials exceeded this threshold.
Reductions in both positive and negative subscales are critical. Often, antipsychotic drugs can ameliorate positive symptoms (e.g., hallucinations, delusions) more effectively than negative symptoms (e.g., lack of motivation, social withdrawal). The reductions in the PANSS negative subscale and Marder factor subscale indicate that KarXT may also be effective for negative symptoms, which is promising given that these symptoms are traditionally harder to treat.
The reductions in PANSS total scores and subscale scores are comparable to or even better than many existing antipsychotic medications. Many antipsychotics demonstrate a reduction of 10-20 points on the PANSS total score in clinical trials. The consistent and clinically significant reductions in both positive and negative symptoms are particularly notable.
The side effects reported for KarXT, like constipation, nausea, and headache, are relatively mild and consistent across trials. Importantly, it doesn't seem to have severe adverse events directly attributed to the drug. The profile is different from many existing antipsychotics, which can have side effects such as weight gain, metabolic changes, or extrapyramidal symptoms.
The data indicates that KarXT has an early onset of action (from Week 2) and maintains its efficacy throughout the trial. Early symptom reduction can be crucial for patient adherence and overall well-being.
The findings suggest KarXT, with its unique mechanism of action, may offer a new class of medicine for schizophrenia patients, potentially the first in over 50 years.
Karuna Therapeutics plans to submit a New Drug Application (NDA) to the U.S. FDA in mid-2023. If approved, it could be launched in the second half of 2024.
Reproducibility concerns
While the KarXT data are encouraging, schizophrenia poses some unique clinical trial design challenges that can impact reproducibility. Here are a few study design elements employed for the KarXT Phase 3 program that could impact reproducibility of the result:
- Stringent Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria: While rigorous criteria ensure a well-defined study population, they can also result in a sample that is not representative of the general population with schizophrenia. If the participants are not representative, reproducing the trial in a broader population may yield different outcomes.
- Washout Periods: The washout periods for antipsychotics could lead to significant symptom exacerbation, which could not only affect the baseline state from which improvements are measured but also impact dropout rates. In a different trial where the washout period is managed differently, the results might vary.
- Inpatient Setting Requirement: Conducting the study exclusively in an inpatient setting controls for many environmental variables. However, it might also result in outcomes that differ from what would be observed in an outpatient setting where patients face everyday stresses and variable adherence to medication regimens.
- Language and Literacy Requirements: Limiting participation to individuals fluent in English might exclude non-English speakers who could respond differently to the treatment due to cultural, genetic, or environmental factors.
- Lack of Diversity: The requirement for a stable living situation and a reliable informant may bias the sample towards a more socioeconomically stable and possibly less ethnically diverse population, which might not reflect the broader schizophrenia population.
- Assessment Tools: The use of specific assessment tools, like the PANSS, to measure outcomes means that these tools must be applied consistently across trials. Variability in how assessments are conducted could affect reproducibility.
- Exclusion of Co-occurring Disorders: Many individuals with schizophrenia have co-occurring disorders. By excluding these individuals, the trial may not capture the full spectrum of therapeutic response and side effects experienced in the broader population.
- Exclusion Based on Prior Treatment Response: Excluding patients based on prior treatment resistance or the need for clozapine could eliminate a subgroup that is particularly challenging to treat. If subsequent trials include these patients, the results may not be reproducible.
- Ethical and Safety Concerns: The criteria related to ethical and safety considerations are critical, but they must be balanced against the risk of selecting a population that may not exhibit the full range of challenges and behaviors seen in all patients with schizophrenia. If a subsequent trial adopts less restrictive safety criteria, the results might differ.
The easiest way to build DCF models
Build robust biotech valuation models in the browser. Then download a fully built excel model, customized with your inputs.
ML-007C-MA market opportunity
Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder affecting more than 21 million people worldwide. It is characterized by distortions in thinking, perception, emotions, language, sense of self, and behavior. The socio-economic burden of schizophrenia is significant, encompassing both direct medical costs and indirect costs, including loss of productivity and the need for caregiver support.
Current treatments for schizophrenia primarily target the dopamine D2 receptors. Typical (first-generation) antipsychotics like haloperidol and atypical (second-generation) antipsychotics like risperidone, olanzapine, and aripiprazole are the mainstays of treatment. These antipsychotics are more effective for the positive symptoms (e.g., hallucinations, delusions) but are often less effective for the negative symptoms (e.g., apathy, lack of emotion) and cognitive symptoms. Side effects like extrapyramidal symptoms, weight gain, metabolic syndrome, and tardive dyskinesia are concerns with current treatments.
There's a significant unmet need for treatments that effectively address the negative symptoms of schizophrenia, as these symptoms are often resistant to current antipsychotics and significantly impair quality of life. Many patients discontinue medications due to intolerable side effects or the perceived risk of side effects, which contributes to relapse. Improving cognitive function remains a high priority since it's linked to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
KarXT, with its unique mechanism as an M1/M4 muscarinic agonist, has shown promise in addressing both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia, potentially placing it in a favorable market position. If approved, it could redefine the standard of care and become a first-line therapy, especially for patients with pronounced negative symptoms or those intolerant to current antipsychotics.
As ML-007C-MA shares a similar mechanism of action (being an M1/M4 muscarinic agonist), it will likely compete directly with KarXT. To carve a significant market share, ML-007C-MA would need to differentiate itself, either through superior efficacy, a better side-effect profile, cost, or other factors. If KarXT gets to the market first, it will have a first-mover advantage, and ML-007C-MA will need to clearly demonstrate added benefits to displace it or capture a significant portion of the market.
Below is a revenue build for ML-007C-MA in schizophrenia:
- Patient Population: About 1% of the U.S. population is diagnosed with schizophrenia. With a population of approximately 330 million, that gives us 3.3 million patients.
- Line of Therapy: Given the unmet need for treatments that address negative symptoms and have a better side effect profile, ML-007C-MA might find its place as a second-line therapy after failure or intolerance to the first-line antipsychotics. Over time, with physician comfort and positive real-world evidence, it might transition to a first-line option for a subset of patients.
- Patient Adherence: While schizophrenia is a chronic condition, patient adherence to medication can be variable. The reasons can range from side effects, lack of perceived benefit, and cognitive deficits related to the disease. Let's assume that 70% of the diagnosed patients are adherent to their medications, which is on the higher end of reported adherence rates.
- Diagnosis Rate: Not everyone with schizophrenia receives a formal diagnosis, primarily due to stigma, lack of healthcare access, or misdiagnosis. Based on various studies, we can assume that around 80% of those with the condition get diagnosed and potentially seek treatment.
- Rate of Patients with Appropriate Insurance: Insurance plays a significant role in medication access. While Medicaid covers many individuals with schizophrenia, not all may have access to newer branded medications. Let's conservatively estimate that 75% of those diagnosed have insurance that would cover ML-007C-MA.
- Patient Attrition: Considering the chronic nature of schizophrenia and the fact that many patients switch or discontinue medications, we might see a yearly attrition rate of about 10%. This reduces our patient number to 297,000 in the first year post-launch.
- Pricing: Branded antipsychotics can range in price from $300 to $1000+ per month. If ML-007C-MA offers superior benefits or even comparable benefits with fewer side effects, a pricing range between $1,200 to $1,500/month (or $14,400 to $18,000 annually) might be more justifiable.
- Gross to Net Discounts: Typically, branded medications have gross to net discounts, including rebates, of around 30%. Therefore, the net price for ML-007C-MA might be around $12,600 annually per patient.
- Peak Sales Estimation: Given the competitive landscape, especially with KarXT and other established antipsychotics, let's assume ML-007C-MA reaches peak sales with a market share of 15%. This would give us approximately 207,900 patients, considering some might have switched from KarXT or other antipsychotics. Peak Sales: 207,900 patients x $12,600 = $2.6 billion.
- Competitive Threats: As more patients and physicians become comfortable with KarXT, ML-007C-MA's growth might be affected unless it can showcase superior efficacy, better side effects, or some other unique selling point. Additionally, newer molecules or treatment modalities like digital therapies, psychedelics, etc., might pose a competitive threat in the future.
ML-007C-MA has a significant market opportunity in the U.S., with potential peak sales of over $2.6 billion. However, this is contingent on several factors including its ability to differentiate from competitors, market dynamics, and the evolving standard of care in schizophrenia.
Note: These numbers are hypothetical and based on assumptions. The actual market dynamics, pricing negotiations, and competitive landscape might alter these projections. Always consult with a market research firm or financial analyst for precise forecasting.
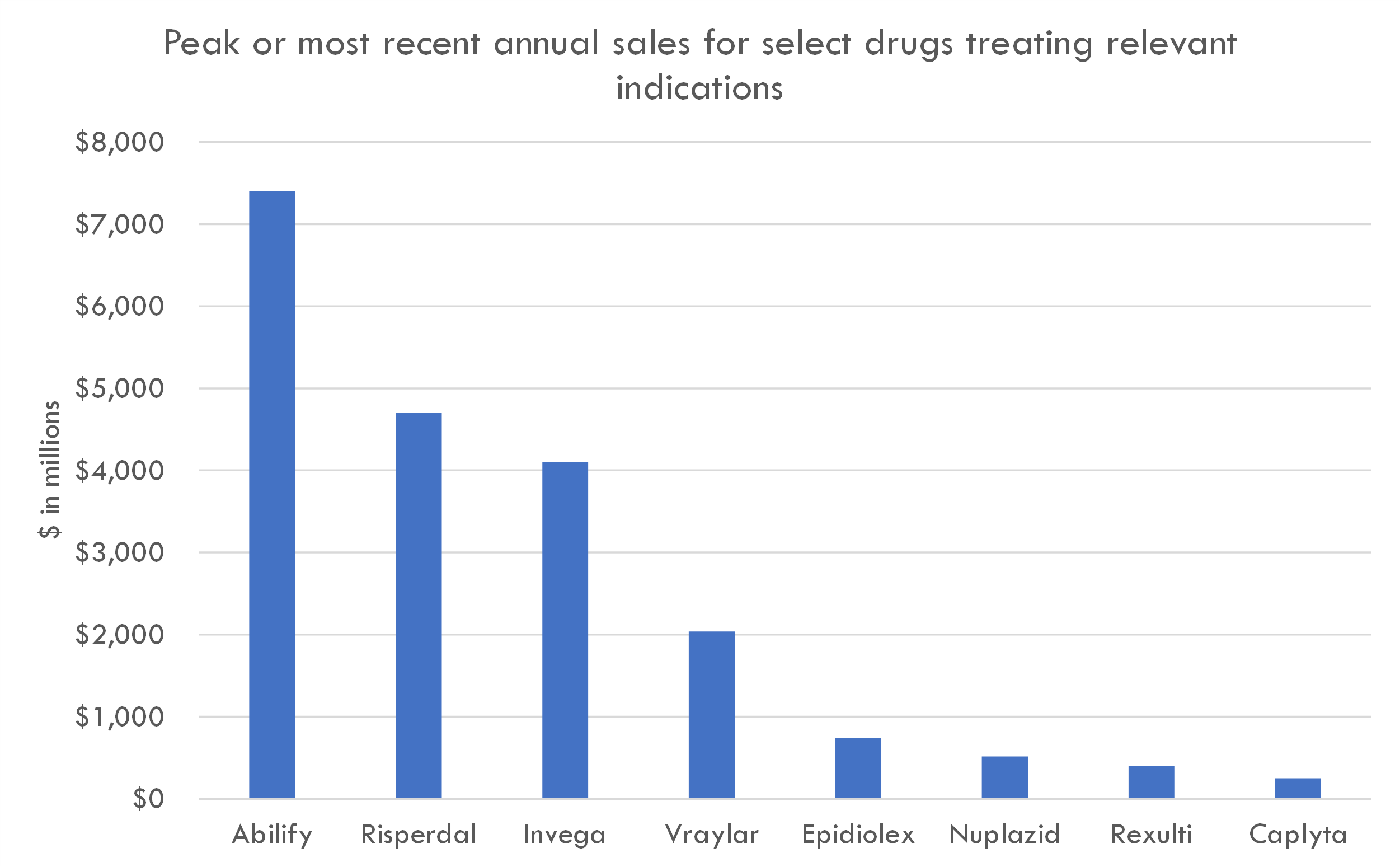
When considering the pricing of antipsychotic medications, especially novel agents targeting unmet needs within schizophrenia, it's useful to look at the pricing of other novel agents within the antipsychotic and CNS (central nervous system) space. Here are some examples of branded antipsychotic medications and their launch prices or current prices in the U.S.:
- Rexulti (brexpiprazole): Developed by Otsuka and Lundbeck, this antipsychotic was approved for schizophrenia and as an adjunctive treatment for major depressive disorder. The cost for a monthly supply was approximately $1,100 without insurance.
- Vraylar (cariprazine): Developed by Allergan, this antipsychotic is used for bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. The price was around $1,200 per month without insurance.
- Caplyta (lumateperone): Developed by Intra-Cellular Therapies, it was approved for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults. The price was in the ballpark of $1,300 for a 30-day supply.
- Invega Sustenna and Invega Trinza: These are long-acting injectable forms of paliperidone developed by Janssen. The price for Sustenna ranged from $2,000 to $3,000 per injection, and for Trinza (a three-month injection), it was significantly higher. However, considering they are long-acting injections, the annual cost becomes comparable to daily oral medications.
- Nuplazid (pimavanserin): Developed by Acadia Pharmaceuticals, it's the only FDA-approved treatment for hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson’s disease psychosis. Given its unique indication and lack of direct competitors, it was priced at around $3,000 per month.
These prices provide context for the range that newer antipsychotic agents can command in the market, especially when they offer advantages over existing therapies. Given that ML-007C-MA has a unique mechanism and potential superior efficacy/safety profile in our hypothetical scenario, a pricing range of $750 per month or $9,000 annually, as suggested in the model, seems justifiable when compared to the prices of these other novel agents.
However, it's essential to recognize that the actual price of a drug is influenced by various factors, including clinical trial results, the competitive landscape, cost of development, marketing strategies, negotiations with payers, and anticipated volume of sales.
ML-007C-MA in Alzheimer's disease psychosis
Scientific thesis
Over 40% of individuals with Alzheimer's disease (AD) experience hallucinations and delusions, termed AD psychosis. This is a significant concern as it not only impairs the quality of life for patients but is also linked to a higher likelihood of nursing home placement and increased morbidity and mortality.
No FDA-approved medication specifically targets AD psychosis. As a result, clinicians may resort to prescribing D2 atypical antipsychotics off-label. These drugs, while they can be effective for some psychotic symptoms, come with a range of side effects, including metabolic disturbances, heart issues, and movement disorders. Particularly concerning is the increased risk of death when these drugs are given to elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis.
Given the above challenges, there's a clear unmet medical need for safer and more targeted treatments for AD psychosis.
Therapeutic Rationale for ML-007C-MA
The muscarinic receptors (specifically M1 and M4) are a subset of acetylcholine receptors in the brain. There's evidence suggesting that activation of these receptors can have therapeutic effects in neurological conditions, including AD. By targeting M1 and M4 receptors, ML-007C-MA might offer a mechanism to address AD psychosis that's different from the D2 receptor pathway used by atypical antipsychotics. This alternative pathway could provide therapeutic benefits without the side effects associated with D2 atypical antipsychotics.
Muscarinic agonists can have side effects when they act outside the central nervous system (CNS), i.e., in the periphery. To minimize these potential peripheral side effects, MapLight's drug is co-formulated with a peripherally selective muscarinic antagonist. This means the antagonist acts primarily outside the CNS, blocking unwanted muscarinic activation in the body while allowing the M1/M4 agonist to act within the brain. This approach is designed to optimize the therapeutic benefit in the brain while minimizing side effects in the rest of the body.
Market overview
Here's a hypothetical revenue build for ML-007C-MA for Alzheimer's disease psychosis, focusing on the U.S. opportunity:
- Target Population
- Over 40% of Alzheimer's disease patients experience AD psychosis.
- Over 5 million Americans were living with Alzheimer's disease.
- Target Population: 0.4 * 5 million = 2 million patients.
- Not all cases of Alzheimer's disease psychosis are diagnosed, especially in the early stages. Let's conservatively assume a 75% diagnosis rate: 2 million × 0.75 = 1.5 million 2 million × 0.75 = 1.5 million.
- Let's estimate that 85% of the diagnosed patients have appropriate insurance coverage that would cover a significant portion of the cost of ML-007C-MA: 1.5 million × 0.85 = 1.275 million 1.5 million × 0.85 = 1.275 million.
- Treatment Penetration and Attrition
- With no FDA-approved medications for AD psychosis, there's a significant unmet need, which could mean less competition initially. Assume 30% penetration at peak = 382,500.
- In chronic diseases, adherence can often be lower than expected due to factors like side effects, perceived lack of efficacy, or pill burden. Let's assume a 70% adherence rate, reducing our patient number: 382,500 × 0.70 = 267,750 patients 382,500 × 0.70 = 267,750 patients.
- Patient attrition due to disease progression, side effects, or switching therapies can be estimated at 10% annually, yielding 241,000 patients.
- Pricing
- Given the premium pricing of the drug for schizophrenia and considering the immense unmet need in Alzheimer's disease psychosis, let's use the range of $1,200 to $1,500/month (or $14,400 to $18,000 annually).
- Gross to Net Discounts:
- Discounts, rebates, and returns in the U.S. can be substantial. An estimate of 30% off the list price is a general benchmark but varies by therapy and indication.
ML-007C-MA in dyskinesia
Scientific thesis
Dyskinesias are characterized by involuntary, abnormal, and often repetitive muscle movements that significantly impact a patient's quality of life. Two main types of drug-induced dyskinesias are highlighted: LID (from Parkinson's disease treatment) and TD (from the use of D2 atypical antipsychotics).
Conventionally, treatments might target broader brain regions, which could lead to off-target effects or complications. The issue with many current treatments is that they often have substantial side effects, especially when dopaminergic systems are targeted.
MapLight's therapeutic strategy is to take a more precise approach, targeting only a small subset of neurons in the basal ganglia that show altered activity patterns in dyskinesia cases. By focusing on this specific subset, MapLight hopes to achieve effective treatment without the broader complications seen with more widespread brain-targeting treatments.
These receptors have been implicated in the modulation of neuronal activity within the basal ganglia. Dysregulated activity in the basal ganglia has been associated with dyskinesias. By targeting M1 and M4 receptors, MapLight aims to restore normal neuronal activity patterns in the affected regions without impacting the dopaminergic system, which is often associated with side effects.
The co-formulation with a peripherally selective muscarinic antagonist suggests that MapLight is aiming to enhance the therapeutic benefit of the M1/M4 agonist while minimizing potential side effects. Specifically, the peripheral antagonist would reduce potential muscarinic side effects outside the central nervous system, such as those related to the gastrointestinal or cardiovascular systems.
MapLight's ML-007 program is designed to offer both improved efficacy and reduced side effects compared to current treatment options for drug-induced dyskinesia. This implies that ML-007C-MA might provide a better benefit-risk profile compared to existing treatments.
Market overview
Here, we'll provide a high-level estimate for the US opportunity for ML-007C-MA in dyskinesias based on available data. Note that actual results could vary considerably based on a myriad of factors, including clinical trial outcomes, payer negotiations, competitive launches, and more.
- Levodopa-induced dyskinesia (LID): A large proportion of Parkinson’s Disease (PD) patients develop LID after several years on levodopa therapy. Considering the estimated 1 million people with PD in the US, about 40% might develop LID at some point. This gives a potential target population of 400,000.
- Tardive dyskinesia (TD): The prevalence of TD is estimated to be around 500,000 in the US, bringing the total potential patient pool to 900,000.
- Diagnosis and Insurance Rates: Not every case might be diagnosed, especially if symptoms are mild. Let's assume an 85% diagnosis rate, which brings our number down to 765,000. Let's assume 80% of these diagnosed patients have appropriate insurance coverage: 765,000 × 0.80 = 612,000 765,000 × 0.80 = 612,000.
- Market Penetration: Not every patient will be treated with ML-007C-MA. Given that there are existing treatments for LID and TD (though with side effects), let’s assume a conservative 10% peak market penetration, leading to 61,200 patients.
- Adherence: Chronic treatments often see reduced adherence over time. If we assume a 70% adherence rate, this reduces our number to 61,200 × 0.70 = 42,840 patients 61,200 × 0.70 = 42,840 patients.
- Pricing: Given the pricing set for the schizophrenia indication, let's use the range of $1,200 to $1,500/month (or $14,400 to $18,000 annually).
- Gross to Net Discounts: Assuming the same gross to net discounts as before, a 30% reduction brings our price range down to $10,080 to $12,600 annually.
- Annual Revenue: 61,200 patients * $12,600 = $771 million at peak.
- Competition and Line of Therapy: Competition from other agents might limit the peak sales potential. Existing treatments like amantadine (for LID) and valbenazine or deutetrabenazine (for TD) already exist in the market. If ML-007C-MA proves to have a better efficacy and side effect profile, it might be adopted as a first or second-line treatment, boosting its market share. However, if it has comparable or inferior profiles, it might be reserved for later lines of therapy or niche patient populations.
ML-004 in autism spectrum disorder
Scientific thesis
The serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) system plays a significant role in modulating various neurophysiological and behavioral processes, including mood, aggression, sleep, and appetite. Several lines of evidence suggest that the serotonin system may be dysregulated in autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
It's well-documented that individuals with ASD often have alterations in serotonin levels. In fact, between 25% to 30% of individuals with ASD have elevated blood serotonin levels, a phenomenon known as hyperserotonemia. The underlying reasons for this elevation and its implications for the disorder's pathology remain subjects of investigation.
The 5-HT1B receptor is a presynaptic autoreceptor that regulates serotonin release. When activated, these receptors typically inhibit further serotonin release, effectively modulating its levels in the synapse. In the context of ASD, where serotonin dysregulation might play a role, targeting these receptors can help in fine-tuning serotonin neurotransmission.
Studies in animal models have shown that 5-HT1B receptors play roles in various behaviors, including aggression, impulsivity, and social behaviors. Since individuals with ASD can exhibit challenges in social communication, repetitive behaviors, and sometimes increased irritability or aggression, modulating 5-HT1B activity might influence these behavioral aspects.
ML-004 will be evaluated for its impact on core social communication deficits and irritability in ASD. Given the involvement of the serotonin system in both social behaviors and mood regulation, there's a rationale that a 5-HT1B agonist might address both these aspects.
One advantage of targeting specific serotonin receptors (as opposed to broad modulation of the serotonin system) is the potential for fewer side effects and a better tolerability profile. By being selective, ML-004 might offer therapeutic benefits while minimizing unwanted effects.
Past treatments targeting the serotonin system (like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or SSRIs) have been tested in ASD with mixed results. The specificity of a 5-HT1B agonist might offer a more targeted approach, potentially yielding better efficacy.
Market overview
To estimate the potential revenue for ML-004 in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) for the U.S. market, we'll need to consider a number of variables:
- Prevalence: According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the prevalence of ASD in the U.S. has been on the rise, with the most recent data suggesting about 1 in 54 children are diagnosed with ASD. While this prevalence pertains to children, it's important to note that ASD is a lifelong condition. The clinical trial for ML-004 includes both adolescents and adults. For simplicity, let's assume that 1% of the U.S. population, or approximately 3.3 million people, are potential candidates for treatment.
- Diagnosis Rate: Not everyone with ASD receives an official diagnosis. If we estimate that 70% of individuals with ASD are diagnosed, that would bring our potential treatment population to 2.31 million.
- Treatment Population: Since ML-004 is being evaluated for adults and adolescents with ASD, we'll consider that this segment makes up 50% of the diagnosed population. This leaves us with 1.155 million potential patients.
- Insurance Coverage: Insurance can be a significant barrier to accessing medication. If we assume that 70% of these potential patients have appropriate insurance coverage, that leaves us with about 809,500 patients.
- Market Penetration: Using a conservative estimate, let's say ML-004 captures 10% of the market in the first few years post-launch, or 80,950 patients.
- Patient Adherence: Non-adherence is a significant issue in many chronic conditions. If we assume that only 70% of patients remain adherent to the medication, that would be 56,665 patients.
- Pricing: The pricing of neuropsychiatric drugs can vary widely, but given the unmet need in ASD, a premium pricing might be feasible. Let's assume an annual cost of $20,000 per patient.
- Gross-to-Net Discounts: Factoring in rebates, discounts, and potential payer pushbacks, a gross-to-net discount of around 30% can be expected.
- Patient Attrition: Since ASD is a chronic condition and treatment effects might be more noticeable over a longer term, a slightly lower annual attrition rate of around 8% can be estimated.
- Competition: Currently, there are two FDA-approved medications for irritability associated with ASD: risperidone and aripiprazole. However, neither addresses the core social communication deficits. If ML-004 proves effective for core symptoms, it could have a competitive advantage. However, there's also ongoing research into other potential treatments for ASD, which might provide competition in the future.
With these considerations, and assuming a slow and steady growth in patient numbers due to awareness and acceptance of the treatment, peak sales might reach approximately $1.4-1.6 billion in net revenue annually. Remember, these are rough estimations, and real figures can differ significantly based on actual market dynamics, the results of clinical trials, and other unpredictable factors.
When determining the pricing for a new drug, it's often useful to look at the prices of other drugs that target similar patient populations or offer analogous treatments in terms of value, novelty, and effectiveness. Let's explore a few drugs that are used to treat conditions related to the central nervous system, especially those targeting neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders:
- Aripiprazole (Abilify)
- Indication: Initially approved for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and as an adjunct for depression. Later, it received approval for irritability associated with autistic disorder in pediatric patients.
- Pricing: When it was on-patent, the monthly cost of Abilify was around $900-$1,500 for the oral tablets, which would translate to $10,800-$18,000 annually.
- Risperidone (Risperdal)
- Indication: Used to treat schizophrenia, bipolar mania, and irritability associated with autistic disorder in pediatric patients.
- Pricing: Before it went generic, the monthly cost of Risperdal was several hundred dollars, with annual costs ranging in several thousands.
- Brexpiprazole (Rexulti)
- Indication: Approved as an adjunctive therapy for major depressive disorder and for the treatment of schizophrenia.
- Pricing: The monthly cost can be around $1,100, which equates to $13,200 annually.
- Nuplazid (pimavanserin)
- Indication: Approved for Parkinson’s disease psychosis.
- Pricing: The drug was notably one of the pricier CNS drugs, with an annual cost surpassing $30,000.
- Epidiolex
- Indication: Used for two rare forms of epilepsy and is the first FDA-approved drug that contains a purified substance derived from marijuana (cannabidiol).
- Pricing: The list price was set at $32,500 annually.
It's important to note that while these drugs provide a frame of reference for pricing in the CNS space, the specific pricing for ML-004 would need to take into consideration its efficacy, safety profile, and the unmet need it addresses in the ASD population. If ML-004 offers substantial improvements over existing therapies or addresses aspects of ASD that currently have limited treatment options, it could command a premium price. On the other hand, if its benefits are more modest or if it faces stiff competition in the market, its pricing might be more constrained.
Given the examples, an estimated annual price of $20,000 for ML-004 seems reasonable and within the range of other CNS drugs, especially if it offers significant benefits for ASD patients.
The easiest way to build DCF models
Build robust biotech valuation models in the browser. Then download a fully built excel model, customized with your inputs.